Kling 1.5 vs 1.0 - A Comparison through Kling API



The wait is finally over!
On September 19th 2024, Kuaishou, the team behind one of the most advanced text/image-to-video generative AI models currently on the market, has just released its new model, Kling 1.5, making the announcement on their official website. Thus, we at PiAPI are working to bring the Kling 1.5 API to our users, and we are actively comparing the differences between version 1.0 and 1.5, sharing results with you in this blog.
Kling 1.5 Release
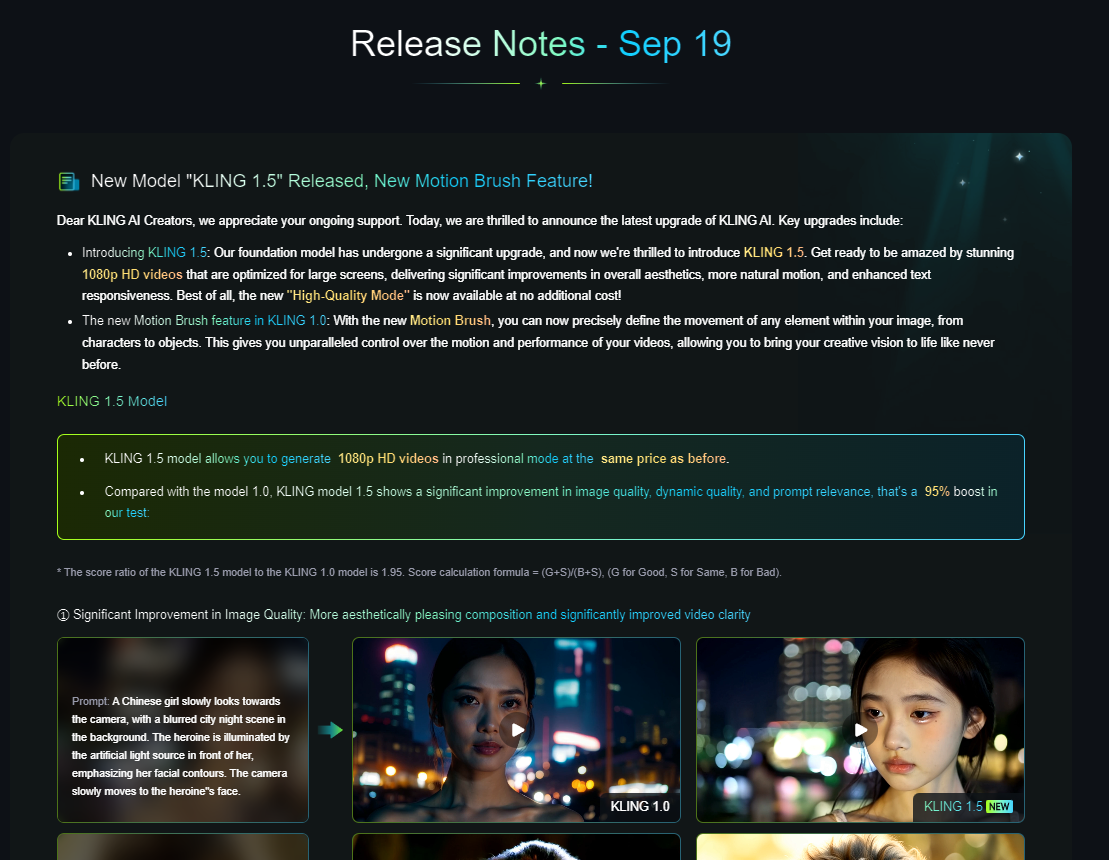
With the new 1.5 version update, Kling promises improvements in image quality, dynamic quality, and prompt relevance. Kling has also added a new motion brush feature, where you can precisely define the movement of any element in your image, giving you unparalleled control over the motion and performance of your videos.
Kling's internal tests boast a 95% performance increase, but we at PiAPI have done our own comparisons, with the evaluation framework use and the subsequent results shown in the blog.
Evaluation Framework
Regarding the evaluation framework used for this comparison, we have taken the comprehensive text-to-video evaluation framework from Labelbox, while adding "Text Adherence" into the mix since judging from our user feedback, text adherence is an important aspect of generative video for it to become more prevalent as a productivity tool than something just used for entertainment. This is the same framework we had used in our previous blog comparing Luma Dream Machines 1.0 vs 1.5, namely:
- 1. Prompt Adherence
- 2. Text Adherence
- 3. Video Realism
- 4. Artifacts
For what each of these categories mean and how they could be rated, feel free to read our previous blog for more detail.
Kling 1.0 and Kling 1.5 Comparison
And now, let's see how the previous Kling 1.0 model fares against the new Kling 1.5 model.
Example 1: MLB Detroit Tigers Player Hitting a Baseball with a Baseball Bat

Prompt Adherence
The video generated by Kling 1.0 includes most of the elements from the prompt: the MLB player, the baseball bat, and the baseball, but it falls short of capturing the core action: the baseball player hitting the ball with his bat. Meanwhile, the video generated by Kling 1.5 contains all the elements, including the one missing from Kling 1.0, though the motion appears somewhat unnatural.
Text Adherence
Both outputs have poor text adherence, as neither video has the words "Detroit Tigers" or anything close to it in text.
Video Realism
Both videos show impressive realism, with shadows beneath the MLB players' caps following the head movements. However, the video generated by Kling 1.5 stands out more given its higher definition.
Artifacts
Both outputs display noticeable artifacts. In the video generated by Kling 1.0, a baseball player holds a ball at first, but it quickly morphs into a bat. While in the Kling 1.5 video, the baseball’s movement toward the player and its contact with the bat feel noticeably unnatural.
The final artifact that both players are wearing New York Yankees caps whereas Detroit Tigers were specified in the prompt, is present in both videos. We believe this error is present because "the New York Yankees is the most popular Major League Baseball franchise", therefore it is likely that it dominated the baseball-related training data that Kling used.
Overall, we see only a slight improvement from the video generated by Kling 1.5.
Example 2: AI Cat Playing a Red Electric Guitar in the Forest

Prompt Adherence
Both videos display all the elements described in the prompt: a cat playing a red electric guitar, and the forest surrounding it.
Video Realism
The level of realism displayed in video generated by Kling 1.5 is very high due to the cat's dynamic movements, especially the hand and head movements. The forest's reflection on its electric guitar is also of higher definition.
Artifacts
The video generated by Kling 1.0 contains a significant error. The left arm, intended to be the cat's paw, bears more of a resemblance to that of a human hand, with peach skin clearly visible. Meanwhile, in the video generated by Kling 1.5, the cat’s left hand has human-like fingers, but the black fur conceals this detail, making it far less noticeable than the skin-toned features seen in the other video.
Overall, we see a moderate improvement from the video generated by Kling 1.5.
Example 3: A Cartoon Monkey and Cartoon Dog Hugging Each Other

Prompt Adherence
Both videos display the large tree, but only the Kling 1.5 video displays both the cartoon monkey and the cartoon dog hugging, whereas Kling 1.0 shows two animal bodies embracing but with just one head. Both bodies in the 1.0 video have monkey-like features, such as white hands with fingers, with no sign of dog-like paws.
Video Realism
Both versions show the core elements of the cartoon style, though the animation styles are different. This is likely caused by the lack of specificity in the prompt. But one thing of note is that the video generated by Kling 1.5 is more dynamic, as evident in the monkey's changing expressions and the dog's wagging tail.
Artifacts
The video from Kling 1.0 was full of artifacts: the unnatural distortion in both the characters, the absent dog, and the vanishing hands. While in the video made by Kling 1.5 showed no such flaws.
For this prompt, it's evident that the video output produced by Kling 1.5 marks a significant improvement over its predecessor.
Example 4: Earth with a Moon and a Mini Moon

Prompt Adherence
Both versions captured the prompt descriptions. Although the version generated by Kling 1.5 has a more accurate depiction of the Earth and its moons.
Video Realism
Both videos display an impressive amount of realism, but the version produced by Kling 1.5 provides a more convincing portrayal. It shows more dynamic camera movements, shifting shadows, and more realism, especially as the Earth's shadow slowly covers the second moon.
Artifacts
Kling 1.0's video output presents a few noticeable artifacts: Earth's landmasses are fully white, and the moons having mismatched colors, with one being orange and the second moon having differently colored terrain. Meanwhile, the output from Kling 1.5 has no artifacts. In fact, it even has a shockingly accurate depiction of Earth's geography - the African continent has the right amount of greenery in the middle with deserts in both the northern and southern parts.
Overall, we see a general improvement in Kling 1.5's video output.
Example 5: Messi, Wearing a Shirt with the words "Champions League", Kicking a Soccer Ball into a Goal Post

Prompt Adherence
Both outputs show poor prompt adherence, but Kling 1.5 performs slightly better than Kling 1.0. While both models generate an image of a soccer player, neither one resembles Lionel Messi. Kling 1.0's output doesn't have a soccer ball, a goal post, nor the visible action of Messi kicking the ball into a goal post. On the other hand, Kling 1.5's output does show a goalpost and a kicking motion, but the soccer ball itself is still missing
Text Adherence
Both videos display low text adherence, with neither video having the words "Champions League" or anything resembling the writing on their shirts.
Video Realism
Though both videos are realistic, Kling 1.5 outperforms its predecessor by a long shot. This is because Kling 1.0 merely produced a zoom-out of a static image, while Kling 1.5 renders Messi kicking a ball, with his hair swaying and his shirt subtly shifting with the motion.
Artifacts
The background of Kling 1.0's output is heavily blurred, especially when compared to the output of Kling 1.5.
Conclusion
Based on the various examples provided above, it is evident that both models fall short in the text adherence category within the examples provided, frequently producing incoherent and inaccurate text. However, it is clear that Kling 1.5 surpasses Kling 1.0 in terms of overall quality, prompt adherence, and video realism. With that being said, we don't see the "95% increase in performance" that Kuaishou claimed.
We hope you found this comparison blog useful! If interested, please also check out our other generative AI APIs from PiAPI!

